MEarthSci (Hons) at University of Manchester
1st class (2015-2019)
HSK1 eqv. Mandarin & Chinese Culture Zhejiang University
Distinction (2019)
PhD E4DTP NERC University of Edinburgh
(2019-2023)
1st class (2015-2019)
HSK1 eqv. Mandarin & Chinese Culture Zhejiang University
Distinction (2019)
PhD E4DTP NERC University of Edinburgh
(2019-2023)
Current Biology
|
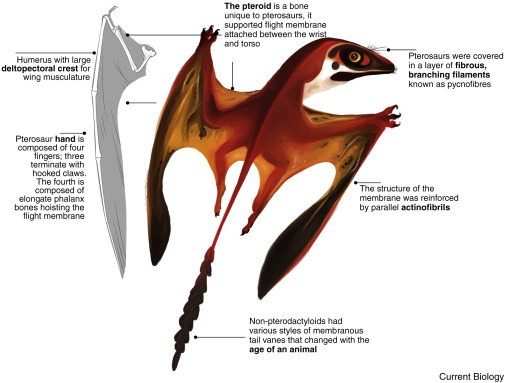
Pterosaurs were the first vertebrates to evolve flight and include the largest flying animals in Earth history. While some of the last-surviving species were the size of airplanes, pterosaurs were long thought to be restricted to small body sizes (wingspans ca. <1.8–1.6 m) from their Triassic origins through the Jurassic, before increasing in size when derived long-skulled and short-tailed pterodactyloids lived alongside a diversity of birds in the Cretaceous. We report a new spectacularly preserved three-dimensional skeleton from the Middle Jurassic of Scotland, which we assign to a new genus and species: Dearc sgiathanach gen. et sp. nov. Its wingspan is estimated at >2.5 m, and bone histology shows it was a juvenile-subadult still actively growing when it died, making it the largest known Jurassic pterosaur represented by a well-preserved skeleton. A review of fragmentary specimens from the Middle Jurassic of England demonstrates that a diversity of pterosaurs was capable of reaching larger sizes at this time but have hitherto been concealed by a poor fossil record. Phylogenetic analysis places D. sgiathanach in a clade of basal long-tailed non-monofenestratan pterosaurs, in a subclade of larger-bodied species (Angustinaripterini) with elongate skulls convergent in some aspects with pterodactyloids. Far from a static prologue to the Cretaceous, the Middle Jurassic was a key interval in pterosaur evolution, in which some non-pterodactyloids diversified and experimented with larger sizes, concurrent with or perhaps earlier than the origin of birds.
|

|
Current Biology
|
[SVP 2020] AN EXCEPTIONALLY WELL PRESERVED PTEROSAUR FROM THE MIDDLE JURASSIC OF SCOTLAND
Natalia Jagielska; Stephen.Brusatte; Michael O'Sullivan; Ian Butler; Tom Challands; Neil Clark; Nick Fraser; Amelia Penny; Dugald Ross; Mark Wilkinson
An incomplete fossil record limits understanding of pterosaurian macroevolution during the Middle Jurassic, a period associated with diversification of many major pterosaur clades. The European Middle Jurassic pterosaurian record, until now, has consisted of numerous non-taxon specific specimens and included a single named genus, based on a partially preserved dentary. Here we describe a new three-dimensionally preserved partial skeleton from the Bathonian Lealt Shale Formation of Skye, Scotland that helps fill the Middle Jurassic pterosaur gap. It is the most complete fossil from the Jurassic sequence of the Scottish Hebrides, which commonly yields ichnofossils but only fragmentary archosaur remains, and the first nearly complete Middle Jurassic pterosaur from outside of China. The new pterosaur is mostly articulated and includes the skull (which retains delicate palatal, hyoid, and neurocranial elements), complete cervical and caudal vertebral series, fully preserved paired forelimbs with partially preserved wing phalanges, a disarticulated dorsal vertebral series and ribcage, and a poorly preserved sacral, pelvis and hindlimb region. It is the largest non-pterodactyloid on record, with an estimated 2 m wide wingspan. The specimen represents a new genus and species diagnosed by several autapomorphies, including slender, curved humeral shaft; large teardrop-shaped lower temporal fenestra; a novel "jugo-lacrimal" fossa, and unique palatal arrangement with trident-shaped anterior vomer. We conducted a phylogenetic analysis by combining several published datasets, which placed the new Scottish pterosaur within the paraphyletic array of non-monofenestratans commonly called the Rhamphorhynchinae, where it shares cranial similarities to the similarly-aged Chinese Angustinaripterus longicephalus. We imaged the skull using microCT, which reveals a brain endocast with a large cerebellum and floccular region wrapped by thin, curved semi-circular canals of the inner ear, similar to closely related Rhamphorhynchus muensteri. Along with the highly diverse but fragmentary Tayton Limestone Formation assemblage of England, the new specimen challenges the long-considered notion that the European Middle Jurassic was a time of low pterosaur diversity and anatomical disparity.
[PALASS 2020] NEW, UNIQUE PTEROSAUR REMAINS FROM THE GREAT ESTUARINE GROUP OF SCOTLAND
Natalia Jagielska, Stephen L. Brusatte, Michael O’Sullivan, Ian Butler, Thomas J. Challands, Neil D. L. Clark, Nicholas C. Fraser, Amelia M. Penny, Dugald A. Ross and Mark Wilkinson
The European Middle Jurassic is one of the largest gaps in the pterosaurian fossil record. It is a period of apparent diversification, introducing the successful monofenestratan bauplan. Our discovery, a three-dimensionally preserved Bathonian non-pterodactyloid pterosaur, provides essential data for this time gap. The new pterosaur originates from the Middle Jurassic Lealt Shale Formation of Skye, Scotland. This formation is recognized for prolific dinosaurian ichnofossils and is a part of the fossiliferous Great Estuarine Group. The fossils originating from the Hebridean Jurassic are mostly partial, the good preservation of our pterosaur is therefore anomalous. It is one of the most complete vertebrate fossils from the Scottish Jurassic and is among the best-preserved pterosaurs from Britain, on par with Dimorphodon from 1828. The specimen represents a new genus and species of Rhamphorhynchinae, with autapomorphies including a slender humeral diaphysis and a large oval fossa on the lacrimal process of the jugal. The pterosaur fills the time gap between Toarcian Posidonia Shale and Tithonian Solnhofen Limestone. It helps to contextualize the largely disarticulated coeval Stonesfield material from Oxfordshire. Ongoing taxonomic research on the specimen will widen our understanding of major shifts in pterosaurian evolution.
Natalia Jagielska, Stephen L. Brusatte, Michael O’Sullivan, Ian Butler, Thomas J. Challands, Neil D. L. Clark, Nicholas C. Fraser, Amelia M. Penny, Dugald A. Ross and Mark Wilkinson
The European Middle Jurassic is one of the largest gaps in the pterosaurian fossil record. It is a period of apparent diversification, introducing the successful monofenestratan bauplan. Our discovery, a three-dimensionally preserved Bathonian non-pterodactyloid pterosaur, provides essential data for this time gap. The new pterosaur originates from the Middle Jurassic Lealt Shale Formation of Skye, Scotland. This formation is recognized for prolific dinosaurian ichnofossils and is a part of the fossiliferous Great Estuarine Group. The fossils originating from the Hebridean Jurassic are mostly partial, the good preservation of our pterosaur is therefore anomalous. It is one of the most complete vertebrate fossils from the Scottish Jurassic and is among the best-preserved pterosaurs from Britain, on par with Dimorphodon from 1828. The specimen represents a new genus and species of Rhamphorhynchinae, with autapomorphies including a slender humeral diaphysis and a large oval fossa on the lacrimal process of the jugal. The pterosaur fills the time gap between Toarcian Posidonia Shale and Tithonian Solnhofen Limestone. It helps to contextualize the largely disarticulated coeval Stonesfield material from Oxfordshire. Ongoing taxonomic research on the specimen will widen our understanding of major shifts in pterosaurian evolution.
[PROGPAL 2020] FOSSIL ANALYSIS FOR THE NEW AGE: A CHEMICAL, TAXONOMIC AND ANATOMIC ASSESSMENT OF A ZYGODACTYLID AVIAN (TCMI 2018.82.1) FROM THE GREEN RIVER FORMATION (EOCENE)
Natalia Jagielska, Roy Wogelius, Phil Manning, Victoria Egerton
Zygodactylidae are a clade of small extinct perching birds from Eocene, distinguished by zygodactylous (parrot-like) digit arrangement. Zygodactylidae are related to the successful extant avian orders Passeriformes (finches) and Psittaciformes (parrots); and are pivotal to the understanding of modern bird evolution. Despite their essential position on the avian evolutionary tree, Zygodactylidae remain relatively understudied. TCMI 2018.82.1 is a complete, articulated fossil of an unknown Zygodactylid hailing from the Green River Formation (Wyoming, North America). The stellar preservation of the fossil prompted the use of the de novo analytical technique, Synchrotron Rapid Scanning X-ray Fluorescence (SRS XRF), to map endogenous chemical proxies providing clues to taphonomy and biology of the organism. This is a first detailed anatomical and chemical assessment of TCMI 2018.82.1. Reduced sternum and keel, roughbone texture, diminutive size and relatively large cranium suggest TCMI 2018.82.1 being the youngest Zygodactylid on the record.The chemical analysis aided the separation of the skeleton from the matrix, but also established phosphorous, iron and zinc asendogenous to the skeletal remains. The chemical traces can be treated as biomarkers, however, due to the strong influence of post-depositional oxidising fluids introducing ferric iron and manganese in slab fractures, complicates the process. The chemicalanalysis differentiated endogenous organic remains from exogenous components of the matrix and oxidising precipitate, illustrating the complexity of the taphonomic processes.SRS-XRF scans demonstrate the importance of fossil study under more than visible light and help to shed the light on the early avian evolution.
Natalia Jagielska, Roy Wogelius, Phil Manning, Victoria Egerton
Zygodactylidae are a clade of small extinct perching birds from Eocene, distinguished by zygodactylous (parrot-like) digit arrangement. Zygodactylidae are related to the successful extant avian orders Passeriformes (finches) and Psittaciformes (parrots); and are pivotal to the understanding of modern bird evolution. Despite their essential position on the avian evolutionary tree, Zygodactylidae remain relatively understudied. TCMI 2018.82.1 is a complete, articulated fossil of an unknown Zygodactylid hailing from the Green River Formation (Wyoming, North America). The stellar preservation of the fossil prompted the use of the de novo analytical technique, Synchrotron Rapid Scanning X-ray Fluorescence (SRS XRF), to map endogenous chemical proxies providing clues to taphonomy and biology of the organism. This is a first detailed anatomical and chemical assessment of TCMI 2018.82.1. Reduced sternum and keel, roughbone texture, diminutive size and relatively large cranium suggest TCMI 2018.82.1 being the youngest Zygodactylid on the record.The chemical analysis aided the separation of the skeleton from the matrix, but also established phosphorous, iron and zinc asendogenous to the skeletal remains. The chemical traces can be treated as biomarkers, however, due to the strong influence of post-depositional oxidising fluids introducing ferric iron and manganese in slab fractures, complicates the process. The chemicalanalysis differentiated endogenous organic remains from exogenous components of the matrix and oxidising precipitate, illustrating the complexity of the taphonomic processes.SRS-XRF scans demonstrate the importance of fossil study under more than visible light and help to shed the light on the early avian evolution.
[SVPCA, 2018] A STUDENT-STAFF-MUSEUM COLLABORATION TO RESTORE, IMAGE AND DISPLAY THE SKELETON OF A LOWER CRETACEOUS ORNITHOPOD DINOSAUR (TENONTOSAURUS TILLETTI LL.1227)
Matthew Dempsey, Natalia Jagielska, Jake Atterby
Originally unearthed from theLower Cretaceous Cloverly Formation of Montana, the Tenontosaurus tilletti specimen LL.1227 was the centrepiece of the Manchester Museum fossil gallery from 1999 to 2004. The skeleton is estimated to be approximately 70% complete, with the most notable missing elements being the hemal arches of the tail and the outer cranial frame (both of which were restored by the original preperators). LL.1227 was a popular addition to the gallery, but the original mount contained multiple anatomical inaccuracies –mostnotably the tripodal tail-dragging stance and the strongly pronated forelimbs. Several incomplete elements (particularly the forelimbs) were artificially extended apparently without reference to the well-documented literature on the species. Many of theseelements remain glued to the now-dismantled material currently in the University of Manchester’s storage. As Tenontosaurus tilletti is an extensively known species, there is little novel research that can be carried out on the LL.1227 specimen. However, the skeleton has provided a unique opportunity for student-staff-museum collaboration and community outreach. We present our progress on fully documenting, restoring and remounting the LL.1227 specimen, which is eventually planned to be re-displayed to modern standards in a renovated section of the Manchester Museum. A particular highlight of this student-led project is the high specification 3D imaging of the specimen using photogrammetry via Agisoft Photoscan. This will allow us to create a 3D print of the skeleton for mounting within the University, and provide a high quality open-source model for research purposes.
Matthew Dempsey, Natalia Jagielska, Jake Atterby
Originally unearthed from theLower Cretaceous Cloverly Formation of Montana, the Tenontosaurus tilletti specimen LL.1227 was the centrepiece of the Manchester Museum fossil gallery from 1999 to 2004. The skeleton is estimated to be approximately 70% complete, with the most notable missing elements being the hemal arches of the tail and the outer cranial frame (both of which were restored by the original preperators). LL.1227 was a popular addition to the gallery, but the original mount contained multiple anatomical inaccuracies –mostnotably the tripodal tail-dragging stance and the strongly pronated forelimbs. Several incomplete elements (particularly the forelimbs) were artificially extended apparently without reference to the well-documented literature on the species. Many of theseelements remain glued to the now-dismantled material currently in the University of Manchester’s storage. As Tenontosaurus tilletti is an extensively known species, there is little novel research that can be carried out on the LL.1227 specimen. However, the skeleton has provided a unique opportunity for student-staff-museum collaboration and community outreach. We present our progress on fully documenting, restoring and remounting the LL.1227 specimen, which is eventually planned to be re-displayed to modern standards in a renovated section of the Manchester Museum. A particular highlight of this student-led project is the high specification 3D imaging of the specimen using photogrammetry via Agisoft Photoscan. This will allow us to create a 3D print of the skeleton for mounting within the University, and provide a high quality open-source model for research purposes.
OTHER RESEARCH TOPICS
|
DID THE RED SEA DRAW-DOWN DURING THE OLIGOCENE-MIOCENE DESICCATION PHASE (BP INTERNSHIP, 2017)
With Neil Mitchell
|
BP Summer Internship, 2017; involved primary data collection via GIS i.e. ArcMap/ArcGIS; findings resulted in a successful elevator pitch with poster seminar
Funding secured: £2500
|